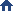
Chemical Process
Distillation
Distillation is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by selective boiling and condensation.

- Operating Pressure : 0.1 mbar ~ 20 mbar
- Configuration of a typical Vacuum Pump System
- Inlet Condenser
- Separator or Knock-Out Pot
- Inlet Isolation Valve, Flame Arrester
- Screw Dry Vacuum Pump
- Flame Arrester, Jacket Type Exhaust Silencer or Exhaust Condenser
Evaporation
Vacuum evaporation is the process of causing the pressure in a liquid-filled container to be reduced below the vapor pressure of the liquid, causing the liquid to evaporate at a lower temperature than normal.
The vacuum evaporation treatment process consists of reducing the interior pressure of the evaporation chamber below atmospheric pressure.
there are other technical advantages such as the ability to distill other liquids with high boiling points and avoiding the decomposition of substances that are sensitive to temperature, etc.
The vacuum evaporation treatment process consists of reducing the interior pressure of the evaporation chamber below atmospheric pressure.
there are other technical advantages such as the ability to distill other liquids with high boiling points and avoiding the decomposition of substances that are sensitive to temperature, etc.

- Operating Pressure : 0.1 mbar ~ 50 mbar
- Configuration of a typical Vacuum Pump System
- Inlet Condenser
- Separator or Knock-Out Pot
- Inlet Isolation Valve
- Screw Dry Vacuum Pump
- Jacket Type Exhaust Silencer or Exhaust Condenser
Crystallization
Crystallization is the process by which a solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal.
Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs.
Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs.
- Operating Pressure : 0.1 mbar ~ 50 mbar
- Configuration of a typical Vacuum Pump System
- Inlet Condenser
- Separator or Knock-Out Pot
- Inlet Isolation Valve
- Screw Dry Vacuum Pump
- Jacket Type Exhaust Silencer or Exhaust Condenser
Pervaporation
Pervaporation is a processing method for the separation of mixtures of liquids by partial vaporization through a non-porous or porous membrane.
Typically, the upstream side of the membrane is at ambient pressure and the downstream side is under vacuum to allow the evaporation of the selective component after permeation through the membrane.
Driving force for the separation is the difference in the partial pressures of the components on the two sides.
Typically, the upstream side of the membrane is at ambient pressure and the downstream side is under vacuum to allow the evaporation of the selective component after permeation through the membrane.
Driving force for the separation is the difference in the partial pressures of the components on the two sides.

- Operating Pressure : 1 mbar ~ 50 mbar
- Configuration of a typical Vacuum Pump System
- Inlet Condenser
- Separator or Knock-Out Pot
- Inlet Isolation Valve
- Screw Dry Vacuum Pump
- Jacket Type Exhaust Silencer or Exhaust Condenser
Reaction
Vacuum in the reaction process is necessary to avoid high temperatures, to remove reaction products or to maintain low pressure in the reaction process.

- Operating Pressure : 0.01 mbar ~ 50 mbar
- Configuration of a typical Vacuum Pump System
- Inlet Condenser
- Filter or Separator
- Inlet Isolation Valve
- Flame Arrester
- Screw Dry Vacuum Pump
- Flame Arrester
- Jacket Type Exhaust Silencer or Exhaust Condenser